Scoliosis
Home / Scoliosis
Scoliosis
Get AppointmentWhat is Scoliosis?
The spine needs to be in particular alignment for proper body posture and balance. If seen from behind, the spine has to be in a straight line. A sideways curvature of the spine is called Scoliosis. (Scoliosis comes from a Greek word that means curvature. Scoliosis was first described by the Greeks and Hippocrates was one of the first physicians to treat Scoliosis)
It is primarily classified based on the location of maximum spine deformity: Cervical Scoliosis, Thoracic Scoliosis, and Lumbar Scoliosis. Scoliosis is primarily a problem of developing the skeletal system; however, it can affect the adult spine also.
Causes of Scoliosis:
- Idiopathic Scoliosis: The cause behind the majority of scoliosis is unknown. The majority of scoliosis patients belong to this category. Girls are affected more than boys. Idiopathic Scoliosis also has a genetic component and can run in family.
- Congenital Scoliosis: Some patients have bony abnormalities within the vertebrae, which can lead to abnormal curvature. These curves are usually acute and progress rapidly.
- Neuromuscular Scoliosis: Loss of muscle support to the spine due to inherent problems in muscles or lack of muscle coordination from brain/ nerve problems can also cause scoliosis. There are usually long “C” shaped curves.
- Degenerative Scoliosis: Adult patients may have unequal degeneration of vertebral segments leading to curvature of the spine.
- Secondary Scoliosis: Scoliosis can also be due to uneven destruction of bone by spine infection/ spine fracture/ spinal tumors etc.,
- Syndromic Scoliosis: Various systemic diseases (genetic/ nongenetic) have associates spine deformity, e.g. Marfan Syndrome, Down’s Syndrome, Osteogenesis Imperfecta, Neurofibromatosis, etc.
- Unequal leg length with pelvic obliquity, muscle spasm, slip disc, and rarely psychosomatic issues can also lead to scoliotic curvature of the spine.
- Early Onset Scoliosis: Age less than 10 years,
- Late Onset Scoliosis: more than 10 years to completion of bone growth (16-18 years),
- Adult Onset Scoliosis: After bone growth is completed (age more than 18 years).
Symptoms of Scoliosis:
During the early onset of scoliosis, the patient or the close contacts including the immediate family, relatives, and friends do not notice any symptoms. This is attributed to the nature of the disease as it has very silent in onset and has a slow progression. Generally patient comes to know about scoliosis when he is noticed by someone bare-chested. This would include family, friends, playmates, etc. However, there are few clear-cut scoliosis symptoms that help in establishing the existence of scoliosis in a person.
These Include:
- 1. A discrepancy in the level of both Shoulders. In a scoliosis person, one shoulder may be higher up than the other shoulder depending upon the type of scoliosis he has.
- 2. Abnormal prominence of the shoulder blade. the person will have abnormal prominence of one shoulder blade than the other which will be seen clearly from the back of the patient.
- 3. The curvature of the midline of the spine seen from the back may bend towards one side. The site of curvature also depends on whether the patient has lumbar scoliosis or thoracolumbar scoliosis.
- 4. In scoliosis patients may also have abnormal rib hump on one side because of the rotation of the spine.
- 5. Abnormality in the level of hip joints
Tests and Diagnosis
The doctor will initially take a detailed medical history and may ask questions about recent growth. During the physical exam, your doctor may have your child stand and then bend forward from the waist, with arms hanging loosely, to see if one side of the rib cage is more prominent than the other.
Treatment Options
A range of different options- non surgical (such as injections- nerve root blocks, epidurals, piriformis injection, etc) or surgical may be considered.
Your doctor may also perform a neurological exam to check for:
- Muscle weakness
- Numbness
- Abnormal reflexes
Imaging Tests
X-rays can confirm the diagnosis of scoliosis and reveal the severity of the spinal curvature. If a doctor suspects that an underlying condition — such as a tumor — is causing scoliosis, he or she may recommend additional imaging tests, including:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI uses radio waves and a strong magnetic field to produce very detailed images of bones and soft tissues.
- Computerized tomography (CT): CT scans combine X-rays taken from many different directions to produce more-detailed images than plain X-rays.
- Bone scan: Bone scans involve the injection of radioactive material, which travels to the parts of your bones that are injured or healing.
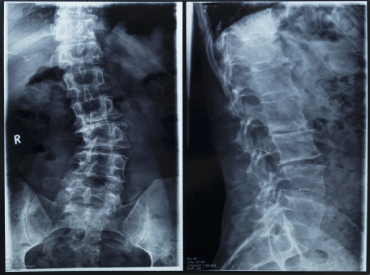
Treatment of Scoliosis:
Treatment for scoliosis generally depends upon the degree of scoliosis, the age at which the patient has presented to a Spine Surgeon, and also the number of complications the scoliosis is currently causing and is supposed to cause in near future.
However the treatment of scoliosis can be grouped into to handful of options which are Observation, Bracing & Scoliosis Surgery discussed under:
- Observation: If the scoliosis spine is very mild, also called a mild curve or simply put Mild scoliosis, and it is not progressive in nature all that is recommended from spine surgeons is to observe the disease and get a regular examination by the treating spine expert. Obviously, that would involve getting periodic Scoliosis radiology X-rays and if the expert desires other scans including CT scans and MRIs can be done. This aids spine surgeons in accurately calculating the extent of disease and also to understand the speed at which it is progressing or it is keeping stable. scoliosis exercises are also taught to the patient.
- Bracing: Functional bracing of the body is done when the surgeon thinks that the curve may progress and may lead to complications. There are various kinds of custom-made scoliosis braces that may somewhat restrict the progress in scoliosis meaning arresting curve by providing strict support to the torso. Types of braces recommended by an expert depend upon whether there is scoliosis of the lumbar spine or thoracolumbar spine. For
- Surgery:Scoliotic curves which are greater than 40 Degrees in angle or which are impending to cause complications in the future, generally need surgical interventions which include Scoliosis correction surgeries and fusion. In these patients detailed preoperative planning is done in order to assess the amount of spinal levels requiring fusion and then the scoliosis surgery is done special Neuromonitoring System. This includes pedicle screw fixation and gradual realignment of the spine in the operation theatre. The aim of surgery is to correct as much as possible the amount of curvature of the spine and also to make sure that the curve does not progress in the future. Thus, avoiding future complications.
GET APPOINTMENT
Schedule Appointment : Your Path to Specialized Care
Get rid of your pain, stress, and enduring with our 24/7 dental services. It's a priority to relieve the pain in surgeon as much as possible. 90% of customers claim that they would come back & recommend us to others.
